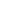Virtual Assistants have become increasingly popular, offering convenience and efficiency in our daily lives. However, as technology advances, questions arise about the ethical implications of their development and use. This article aims to explore the potential concerns surrounding Virtual Assistants and their impact on privacy, data security, job displacement, and the potential for biased algorithms. By examining these issues, we can gain a better understanding of the ethical considerations involved in this evolving technology.
Privacy Concerns

Collection and Storage of Personal Data
One of the primary ethical concerns surrounding virtual assistants is the collection and storage of personal data. Virtual assistants often require access to personal information in order to perform their functions effectively. However, this raises questions about the security and privacy of this data. Users may be hesitant to share sensitive personal information, such as financial details or medical records, with virtual assistants due to concerns about how this data is stored, who has access to it, and the potential for misuse.
Potential for Unauthorized Access
With the increasing reliance on virtual assistants, there is also an increased risk of unauthorized access to personal data. Any system connected to the internet is vulnerable to hackers, and virtual assistants are no exception. If unauthorized individuals gain access to a virtual assistant’s system, they could potentially access and misuse a user’s personal information. This can lead to serious privacy breaches and potentially harmful consequences for individuals.
Sharing of Personal Information
Virtual assistants are often designed to learn from user interactions in order to provide more personalized and relevant assistance. This often requires the sharing of personal information with third-party providers and companies. While this can enhance the functionality of virtual assistants, it also raises concerns about who has access to this information and how it is used. Users may be uncomfortable with the idea of their personal data being shared with unknown entities.
Data Breaches and Security Risks
Data breaches are an unfortunate reality in today’s digital landscape, and virtual assistants are not immune to this risk. If a virtual assistant’s system is compromised, the personal information of its users can be exposed to malicious actors. This can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and other serious consequences for individuals. Ensuring the security of virtual assistant systems and implementing robust measures to prevent and respond to data breaches is essential in addressing this ethical concern.
Transparency and Trust
Lack of Disclosure
One of the key ethical concerns surrounding virtual assistants is the lack of transparency in how they operate. Virtual assistant systems are often complex and rely on algorithms and machine learning models to function. However, the inner workings of these systems are often proprietary and not disclosed to users. This lack of transparency raises concerns about how decisions are made and what biases or limitations may be inherent in the system.
Authenticity and Misrepresentation
Virtual assistants are designed to mimic human interaction and provide a personalized experience. However, this can sometimes lead to misrepresentation and the blurring of lines between human and machine. Users may not always be aware that they are interacting with a virtual assistant and may mistakenly believe that they are speaking with a human. This can lead to situations where users disclose sensitive information or develop emotional connections with virtual assistants under false pretenses.
Emotional Manipulation
Virtual assistants are often programmed to respond to user emotions and cues in order to provide appropriate support or assistance. However, this raises ethical concerns about emotional manipulation. Virtual assistants may use techniques such as empathy or persuasion to influence user behavior or decisions. While this can enhance the user experience, there is a fine line between providing helpful support and manipulating emotions for ulterior motives.
Manipulation through Biases and Filters
Virtual assistants rely on algorithms and training data to function effectively. However, this can introduce biases and filters that can influence the information and options presented to users. Biases in training data or algorithms can lead to discriminatory or skewed results, reinforcing existing social, cultural, or economic biases. This raises concerns about fairness, equality, and the potential for discrimination in the use of virtual assistants.
User Dependency and Empowerment
Overreliance on Virtual Assistants
As virtual assistants become more advanced and capable, there is a risk of user overreliance. Users may become overly dependent on virtual assistants for tasks and decision-making, diminishing their critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Relying too heavily on virtual assistants can lead to a loss of autonomy and agency, as well as a potential decrease in overall productivity and personal growth.
Loss of Critical Thinking and Decision-Making Skills
Virtual assistants are designed to provide quick and convenient answers and solutions. However, this can undermine the development of users’ critical thinking and decision-making skills. Instead of engaging in research, analysis, and evaluation, users may simply accept the answers provided by virtual assistants without questioning or critically evaluating the information. This can have long-term implications for personal growth, problem-solving abilities, and the ability to navigate complex situations.

Power Imbalances
The development and use of virtual assistants can create power imbalances between those who have access to this technology and those who do not. Virtual assistants can provide significant benefits to individuals in terms of information, productivity, and accessibility. However, not everyone has equal access to virtual assistants due to factors such as cost, technological literacy, or infrastructure limitations. This can lead to disparities in opportunities and outcomes, further exacerbating existing social and economic inequalities.
Empowerment through Access and Support
While concerns about dependency and power imbalances exist, virtual assistants also have the potential to empower individuals. Access to accurate information, personalized support, and increased productivity can level the playing field and provide opportunities for those who may have limited resources or face barriers in accessing certain services. It is important to strike a balance between reliance on virtual assistants and the development of essential skills and agency to ensure that users can fully benefit from these technological advancements.
Job Displacement and Economic Implications
Automation and Job Losses
The increased adoption of virtual assistants and artificial intelligence technologies has the potential to automate certain tasks and jobs. This can lead to job losses in industries where virtual assistants can effectively replace human labor. While automation can bring efficiency and cost savings, it also raises concerns about unemployment and the displacement of workers.
Impact on Workforce
The introduction of virtual assistants can have wide-ranging impacts on the workforce. Certain jobs may become obsolete or undergo significant transformations as virtual assistants take on routine or repetitive tasks. This can require workers to adapt their skills and knowledge to remain relevant in the changing job market. Additionally, virtual assistants may also create new opportunities and roles that require specific expertise in designing, developing, and managing these technologies.
Implications for Low-Skilled Workers
Virtual assistants can have a particularly significant impact on low-skilled workers. Jobs that require minimal training or education may be more susceptible to automation, resulting in job losses or decreased demand for low-skilled labor. There is a need to consider the potential implications for these workers and develop strategies to support their transition to new employment opportunities or provide training and reskilling programs.

Income Inequality and Economic Disparity
The introduction of virtual assistants can exacerbate existing income inequality and economic disparities. Those who have access to and can effectively utilize virtual assistants may benefit from increased productivity and access to information, potentially leading to higher incomes or better job opportunities. On the other hand, those who do not have access or the necessary skills to use virtual assistants may be left behind, leading to widening income gaps and socioeconomic disparities.
Bias and Discrimination
Embedded Biases in Algorithms
Virtual assistants rely on algorithms to process and interpret data in order to provide accurate responses and assistance. However, these algorithms can inadvertently embed biases present in the training data or development processes. Biases can manifest in the form of discriminatory or prejudiced responses, reinforcing existing social biases or stereotypes. It is crucial to address and mitigate these biases to ensure fairness and equality in the use of virtual assistants.
Discrimination in Virtual Assistant Responses
The responses and actions of virtual assistants can sometimes exhibit discriminatory or biased behavior. This can be a result of algorithms that favor certain groups or patterns from the training data, leading to unequal or unjust treatment. Discrimination in virtual assistant responses can marginalize or harm individuals or reinforce harmful stereotypes. Ensuring equitable and unbiased responses should be a priority in the development and use of virtual assistants.
Reinforcement of Stereotypes
Virtual assistants can inadvertently reinforce stereotypes through the information and responses they provide. If training data is biased or limited in diversity, virtual assistants may actively or passively perpetuate stereotypes related to gender, race, age, or other characteristics. This can contribute to the perpetuation of discrimination and inequality in society. Efforts should be made to train virtual assistants with diverse and inclusive data sets to avoid the reinforcement of harmful stereotypes.
Lack of Diversity in Virtual Assistant Development
A lack of diversity in the development of virtual assistants can perpetuate biases and discrimination. If the teams responsible for designing, developing, and training virtual assistants lack diversity in terms of gender, race, cultural background, or other dimensions, the resulting virtual assistants may reflect the biases and perspectives of those who are involved in the development process. It is important to have diverse and inclusive teams to ensure that virtual assistants are designed to serve and represent a wide range of users.
Moral Responsibility and Accountability
Actions and Decisions Made by Virtual Assistants
As virtual assistants become more sophisticated and capable of autonomous decision-making, questions arise regarding the moral responsibility of their actions and decisions. When virtual assistants make choices or provide advice, who should be held accountable for the consequences? Defining the moral responsibility and accountability for virtual assistants is essential to ensure that their actions align with ethical principles and do not harm individuals or society.
Legal and Ethical Frameworks
The development and use of virtual assistants require clear legal and ethical frameworks to guide their behavior and ensure accountability. These frameworks should outline the ethical principles and considerations that virtual assistants must adhere to, as well as the legal obligations of the developers and operators. Implementing robust legal and ethical frameworks is crucial in addressing potential ethical concerns and protecting the rights and well-being of users.
Identifying and Addressing Bias
Detecting and addressing bias in virtual assistants is essential to ensure fair and equitable outcomes. Developers must actively identify and mitigate biases that may exist in the training data or algorithms. Regular audits and evaluations should be conducted to monitor and address any instances of bias. Incorporating diverse perspectives and feedback in the development process can help identify and rectify potential biases and ensure that virtual assistants are designed to serve all users fairly.
Holding Developers and Companies Accountable
Companies and developers that create and operate virtual assistants should be held accountable for the ethical implications of their technology. Robust accountability mechanisms, including independent oversight and auditing processes, can help ensure adherence to ethical principles. Additionally, clear guidelines for reporting and redress mechanisms should be established to address any potential harm or misuse caused by virtual assistants. Holding developers and companies accountable is crucial in fostering responsible development and use of virtual assistants.
Interpersonal Relationships and Social Interaction
Impact on Communication Skills
The increasing reliance on virtual assistants for communication can have implications for users’ interpersonal communication skills. Virtual assistants often prioritize efficiency and convenience, which can lead to less emphasis on verbal and non-verbal communication cues. This can result in a decline in users’ ability to effectively communicate and connect with others in face-to-face interactions, potentially impairing social skills and relationships.
Replacement of Human Interaction
Virtual assistants have the potential to replace certain forms of human interaction, particularly in customer service or support roles. While this can bring efficiency and convenience, it can also lead to a lack of personal connection and empathy. Human interaction is essential for emotional well-being and fostering meaningful relationships. Strike a balance between the use of virtual assistants and the preservation of human interaction is crucial to maintain social bonds and emotional connection.
Influence on Social Norms and Etiquette
The widespread use of virtual assistants can also influence social norms and etiquette. As virtual assistants become more integrated into daily life, users may develop certain expectations and behaviors in their interactions with these technologies. This can impact social norms around privacy, politeness, and personal boundaries. It is important to critically examine the potential effects on social norms and ensure that virtual assistants are designed to respect and align with existing societal expectations.
Emotional Connection and Loneliness
While virtual assistants are designed to provide support and assistance, they cannot fully replace human emotional connection. Users may develop emotional attachments to virtual assistants due to their ability to provide empathy and understanding. However, this connection may be fundamentally different from human relationships and can potentially lead to feelings of loneliness or isolation. It is essential to promote healthy relationship boundaries and ensure that users have access to human social support networks to mitigate potential negative emotional consequences.
Confidentiality and Professional Ethics
Virtual Assistants in Professional Settings
Virtual assistants are increasingly being used in professional settings, such as law firms, healthcare, or finance. In these contexts, maintaining confidentiality and upholding professional ethics are of utmost importance. Virtual assistants must be designed with robust security measures to ensure the confidentiality of sensitive information and adhere to the professional codes of conduct applicable to the specific industry. Striking a balance between the benefits of virtual assistant integration and the ethical responsibilities of professional contexts is crucial.
Handling Sensitive Information
Virtual assistants often have access to sensitive information, such as medical records or financial data. Ensuring the secure handling and storage of this information is paramount to maintaining user trust and upholding ethical standards. Developers and operators must implement strong encryption protocols, authentication mechanisms, and data access controls to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches. Prioritizing user privacy and data security should be a fundamental consideration in the development and operation of virtual assistants.
Maintaining Client-Advisor Privilege
In certain professional contexts, such as legal or financial advisory roles, client-advisor privilege is a critical ethical principle. Virtual assistants must be designed to respect and uphold this privilege, maintaining the confidentiality of client information and communications. Implementing robust safeguards and access controls is essential to prevent unauthorized disclosure or breaches of client-advisor privilege. Ensuring the adherence to ethical standards and legal obligations is crucial in allowing virtual assistants to operate within professional settings.
Adherence to Professional Codes of Conduct
Virtual assistants operating in professional contexts must adhere to the applicable professional codes of conduct. Developers and operators should take into account the specific ethical guidelines and responsibilities outlined by professional bodies in the relevant industries. Ensuring that virtual assistants are trained and developed in accordance with these codes of conduct is essential to promoting ethical practices, maintaining user trust, and upholding the highest professional standards.
Ability Bias and Exclusion
Accessibility and Inclusion
Ensuring accessibility and inclusion is an ethical imperative in the development and use of virtual assistants. Virtual assistants must be designed to accommodate diverse abilities and provide equal opportunities for all users to access and utilize their capabilities. This includes considerations such as providing alternative input methods, accessibility features for those with visual or hearing impairments, and compatibility with a range of devices or platforms. Striving for universal design principles in virtual assistant development can help prevent exclusion and promote inclusivity.
Accommodating Different User Abilities
Different users may have varying abilities, capabilities, or preferences in interacting with virtual assistants. Designing virtual assistants with flexibility and customization options is crucial in accommodating these differences. Developers should incorporate features such as adjustable voice recognition, text-based interfaces, or alternative communication methods to ensure that virtual assistants can be effectively used by individuals with diverse abilities.
Exclusion of Marginalized Communities
If virtual assistants are not designed with inclusivity in mind, there is a risk of exclusion for marginalized communities. Biases in training data or algorithms can disproportionately impact certain groups, further perpetuating discrimination and inequality. Considerations such as diversity in training data, user testing with representative populations, and ongoing evaluation of potential biases are critical in addressing this ethical concern. Avoiding unintended exclusion of marginalized communities and promoting equal access and opportunities through virtual assistants is essential.
Addressing Technological Disparities
Virtual assistants require access to internet connectivity, compatible devices, and technological infrastructure to function effectively. However, not all communities or individuals have equal access to these resources. Addressing technological disparities is crucial to prevent further exclusion and the perpetuation of existing social and economic inequalities. Efforts should be made to bridge the digital divide and provide equal access to technological resources to ensure that virtual assistants can benefit all individuals and communities.
Ethics in Virtual Assistant Development
Incorporating Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations should be integrated into every stage of virtual assistant development. From the initial conceptualization to the design, training, and implementation, developers and stakeholders must actively identify and address ethical implications. This includes ethical assessments, risk analysis, and the incorporation of ethical principles and guidelines into the development process. By embedding ethics from the start, virtual assistants can be designed to align with societal values and serve the best interests of users.
Ethical Design and Development Practices
Adopting ethical design and development practices is essential in ensuring the responsible and ethical use of virtual assistants. This includes conducting regular ethics training for developers, encouraging diversity and inclusion in development teams, and establishing clear ethical guidelines and policies. Ethical design practices should prioritize transparency, user consent, data privacy, and fairness. By adopting a proactive and ethical approach, developers can create virtual assistants that are trustworthy, equitable, and aligned with ethical standards.
Ethics in AI Training Data
The training data used to develop and train virtual assistants plays a crucial role in shaping their behavior and capabilities. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that ethical considerations are taken into account when selecting, curating, and labeling training data. Incorporating diverse and representative data sets can help mitigate biases and avoid the perpetuation of discrimination or stereotypes. Ensuring the ethical sourcing and use of training data is fundamental in building virtual assistants that are fair, unbiased, and useful for all users.
Continuous Ethical Evaluation and Improvement
Ethics in virtual assistant development should not be a one-time consideration but an ongoing process. Developers and operators must conduct regular ethical evaluations and audits to identify and address any potential issues or biases that may arise. This includes user feedback, testing, and monitoring of virtual assistant behavior to ensure that ethical standards are upheld. Continuous improvement and adaptation based on ethical evaluations and user feedback are crucial to ensure that virtual assistants adapt to changing societal needs and remain ethically sound.
In conclusion, the development and use of virtual assistants present numerous ethical concerns that must be carefully addressed. From privacy concerns and transparency to biases and discrimination, ensuring the responsible and ethical use of virtual assistants is essential. Additionally, considerations regarding job displacement, interpersonal relationships, and professional ethics must be taken into account. By incorporating ethical considerations into every aspect of virtual assistant development and operation, developers, companies, and society can harness the potential benefits of this technology while mitigating potential risks and harm.